Overview of Medial Retinaculum

The medial retinaculum, also known as the flexor retinaculum, is a thick band of connective tissue that forms the roof of the carpal tunnel in the wrist. It originates from the pisiform bone and triquetrum bone on the ulnar side of the wrist and inserts onto the hamate bone and the hook of the hamate on the radial side. The medial retinaculum serves as a protective sheath for the tendons of the flexor muscles and the median nerve as they pass through the carpal tunnel.
Medial retinaculum is a ligament that binds the flexor tendons of the wrist. Its anatomy and function are intriguing, much like the life of Jerry West. How did Jerry West die ? A tragic loss, yet his legacy in basketball lives on.
Returning to the medial retinaculum, its role in wrist flexion is undeniable, making it a fascinating structure to explore.
Function in Maintaining Carpal Tunnel Integrity
The medial retinaculum plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the carpal tunnel and preventing excessive pressure on the tendons and median nerve. It acts as a firm yet flexible structure that allows for the smooth gliding of the tendons during wrist and finger movements. The retinaculum also helps to prevent the tendons from bowing or dislocating, ensuring their proper alignment within the tunnel.
Clinical Significance of Medial Retinaculum
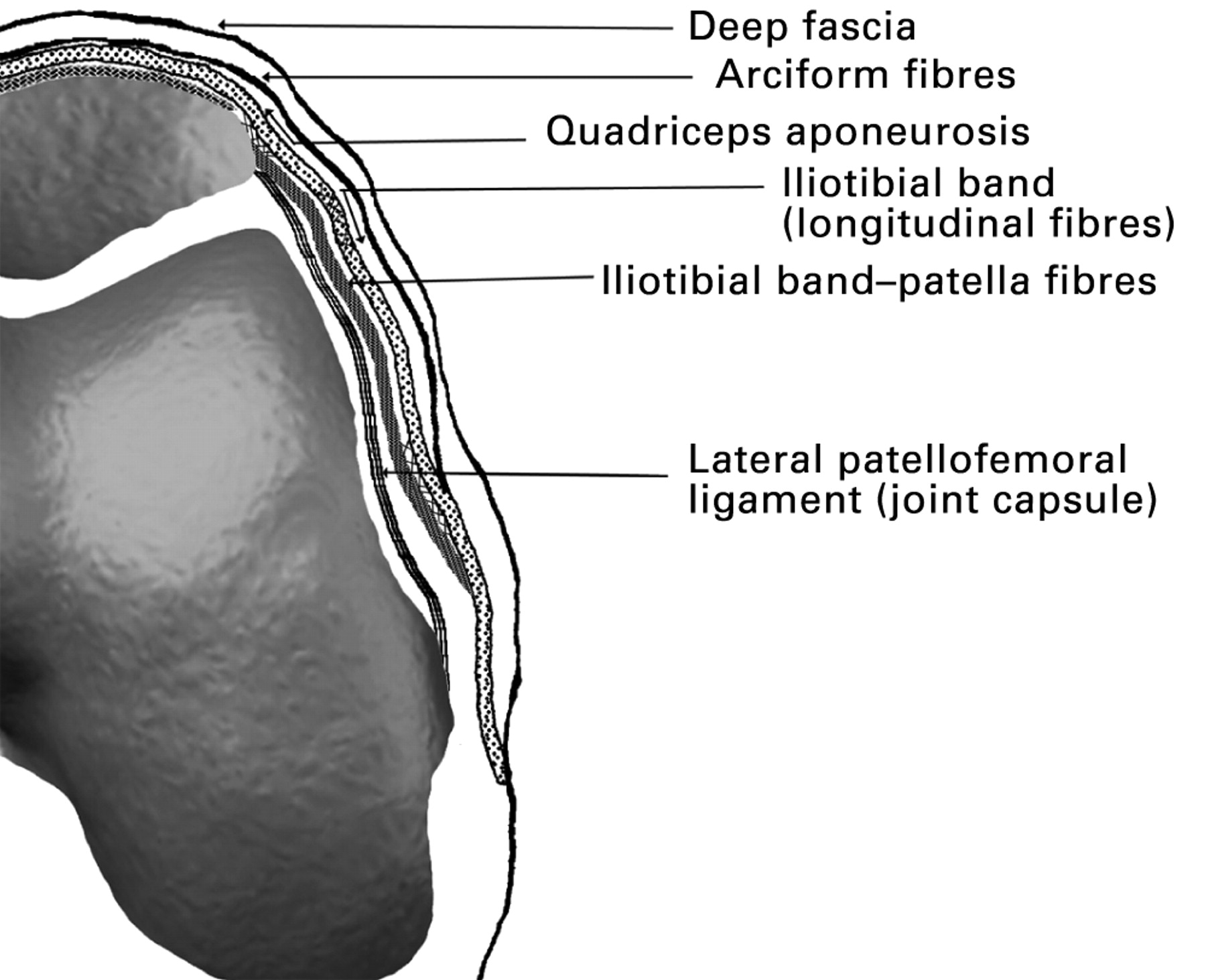
The medial retinaculum plays a crucial role in carpal tunnel syndrome, a common condition that affects the wrist and hand. It acts as a tight band of tissue that covers the carpal tunnel, a narrow passageway through which the median nerve and tendons pass.
When the medial retinaculum becomes thickened or inflamed, it can put pressure on the median nerve, leading to symptoms such as pain, numbness, and tingling in the thumb, index, middle, and ring fingers. This condition is known as carpal tunnel syndrome.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome involves a physical examination and tests such as the Tinel’s sign and Phalen’s test, which check for nerve compression. Treatment options include conservative measures such as wrist splints, corticosteroid injections, and activity modification. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to release the pressure on the median nerve by cutting the medial retinaculum.
Surgical Management of Medial Retinaculum
Surgical release of the medial retinaculum is a common procedure performed to relieve pressure on the median nerve in cases of carpal tunnel syndrome. The surgery involves cutting the transverse carpal ligament, which is a thick band of tissue that runs across the palm of the hand and forms the roof of the carpal tunnel.
Surgical Approaches
There are two main surgical approaches for medial retinaculum release: open surgery and endoscopic surgery.
* Open surgery is the traditional approach, which involves making an incision in the palm of the hand to directly visualize and release the transverse carpal ligament.
* Endoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive technique that uses a small camera and instruments inserted through a small incision to release the ligament.
The choice of surgical approach depends on the surgeon’s preference and the patient’s individual anatomy. Open surgery is generally preferred for more severe cases of carpal tunnel syndrome, while endoscopic surgery is often used for milder cases.
Potential Risks and Complications, Medial retinaculum
As with any surgery, there are potential risks and complications associated with medial retinaculum release. These include:
* Bleeding
* Infection
* Nerve damage
* Scarring
* Persistent pain
The risks of complications are generally low, but it is important to discuss them with your surgeon before undergoing surgery.
The medial retinaculum, a ligament in the wrist, plays a crucial role in stabilizing the carpal bones. While its significance in wrist function is well-known, its connection to the untimely demise of legendary basketball player Jerry West remains a mystery.
For those seeking answers, when did jerry west die provides a comprehensive account of his passing. Returning to the medial retinaculum, its intricate structure and function continue to captivate medical professionals, highlighting its importance in maintaining wrist health.
Medial retinaculum, a connective tissue that stabilizes tendons around the wrist, is like a symphony conductor guiding the movements of the hand. Just as Joe Mazzulla orchestrates the Boston Celtics with finesse and precision, the medial retinaculum ensures the wrist’s smooth and coordinated motion.
The medial retinaculum, a fibrous band in the wrist, plays a crucial role in stabilizing the carpal bones. Its intricate interplay with tendons and muscles ensures smooth hand movements. Speaking of hands, have you heard the latest buzz about James Harden’s love life?
James Harden girlfriend now is making headlines, leaving fans curious about the identity of his special someone. But back to the medial retinaculum, its significance in hand function is undeniable, highlighting the body’s intricate symphony of tissues and their impact on our daily lives.
The medial retinaculum, a band of connective tissue in the wrist, plays a crucial role in stabilizing the wrist joint. Its intricate structure allows for a wide range of movements, from the graceful passes of Patrick Mahomes on the football field to the delicate brushstrokes of an artist.
The medial retinaculum’s韧带功能 ensures that the wrist remains stable and protected during these dynamic movements.